

Next: Relations
Up: THE ARCHITECTURE OF THE
Previous: Multi-level data structures
This section presents the archiecture used in the Festival speech
synthesis system, version 1.3 [3]. The most
significant difference between the Festival architecture and those
using MLDS is that Festival does not constrain linguistic items to be
in linear lists: any graph structure is allowed. Additionally, items
can be contained in more than one structure, which leads to more
efficient representations. We have also generalised the content of an
item such that information of arbitrary complexity can be easily
stored.
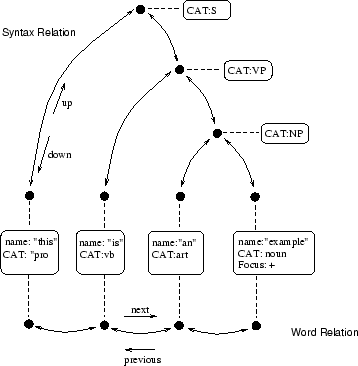
Figure 1:
An example representation of an utterance structure. This
example shows the word relation and the syntax relation. The syntax
relation (shown on top) is a tree with links connecting the nodes,
shown as black circles. The word relation (shown on the bottom) is a
list. The items contain the actual linguistic information and are
shown in the rounded boxes. The dotted lines show the connections
between the nodes and items.
 |
Alan W Black
1999-03-20

