
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net ** This is a COPYRIGHTED Project Gutenberg eBook, Details Below ** ** Please follow the copyright guidelines in this file. **
Title: Sequential Problem Solving
A Student Handbook with Checklists for Successful Critical Thinking
Author: Fredric Lozo
Release Date: August 19, 2005 [eBook #16547]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
***START OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK SEQUENTIAL PROBLEM SOLVING***
Copyright (C) 1998 by F. B. Lozo
Sequential Problem Solving is written for those with a whole brain thinking style. It is for those who seek to validate the propriety of when and under what circumstances they utilize each aspect of their intellect. Sequential Problem Solving helps those with a logical nature to develop creative right brain intuitive processes in a way that can be efficiently utilized by the orderly left brain to develop new solutions to both old and everyday problems. Included are basic study skills for high school and college students.
We are constantly trying to make some sense of our world and the way people treat each other. The purpose of this book is to provide a systematic way of analyzing situations and planning actions.
Sequential Problem Solving is written for those who want to reassure themselves that their thinking is logically correct rather than emotionally or impulsively misguided. It provides step by step procedures for applying computer-like decision making to daily living. Many ordinary problems involve not only physical, concrete parts but also interpersonal elements. Thus problem solving involves both the physical world and the interpersonal world. For instance, when solutions to physical problems are implemented, the job manager must decide which of several leadership-managerial styles is appropriate. Are the workers mature enough and knowledgeable enough to work together as a team without supervision, or are the workers so immature and unruly that an authoritarian task master leadership style will be required, or will the workers need a teacher-leader for some period of time before they become a team?
The underlying principle, throughout Sequential Problem Solving, is an obligation to help each other as citizens of a world community, and an acknowledgement that our real enemy is often ourselves. Our common problem is understanding ourselves in order to be a friend to others. Sequential Problem Solving provides us with a way of checking for the kindness factor in problem solving, with the goal of helping others and being a good citizen in the world community.
A separate section, Dealing with Unattached People, is devoted to the problem of neighbors in the world community who are untrustworthy for some period of time, from the view point that today's enemies are tomorrow's friends.
Some neighbors in the world community are, from time to time, untrustworthy. Since opportunities for misunderstanding are greater in a climate of mistrust, later sections are included that deal with mistrust and ways that we can gauge interpersonal situations and select an appropriate leadership style to match it.
Sequential Problem Solving begins with the mechanics of learning and the role of memorization in learning. The techniques of effective memorization follow, as well as other important learning skills.
This book contains many step by step checklists, much like pilots use to make certain that things of importance are not overlooked. These individual checklists are tied together in a broad flowchart that provides a sequential decision making pathway. The contents of the checklists are things that many adults utilize instinctively, without conscious thought. However these checklist can provide adults with a more positive way of checking their own thinking, in times of stress, and a way for students to become instinctive users of sound logic practices. Teachers may find that students instantaneously begin to act more mature because of the realization that their peers have a common body of knowledge about values and character traits and checklists to evaluate the behavior of others. For teachers, the sequence of presentation here can be readily altered to suit the teachable moment, that moment when a unique, high interest situation arises that lends itself to discussion of a particular topic. The sequence presented here is merely one way in which the various interlocking subjects can be presented.
This presentation is intentionally concise to provide the reader with a composite picture of the use of checklists in logical thinking, without burdening the reader with statistical findings or repetitious historical background information.
The ideas presented here are referenced to credible academic research wherever possible. Endnotes are used extensively to direct the reader to in-depth authoritative resources, and additional references are provided for each section at the back of the book.
In this book I have used the pronoun "he" for humanity in general, rather than using he/she or similar conventions. This usage was selected to enhance the flow of the written word and should not be taken literally. The word "he" is used here to include both women and men and applies to them with equality.
Solving problems is a daily, if not hourly, part of our lives. It is therefore useful to put the mechanics of problem solving and human interpersonal relationships into flowchart form, so that when stress is intense we have some way of making more certain that we are thinking flawlessly. The following is such a flowchart
RESEARCH SKILLS.
RAPID READING.
Effective learners use certain reading techniques [1] that greatly increase both their comprehension and the time required to learn new subjects.
One useful method of reducing new material learning time is the SQ3R method [2]:
Scan.
Question.
Read.
Review.
Recite.
Scanning provides a rapid overview. Many well written books follow logical outlines that can orient the reader to the subject matter. The outline might follow this pattern:
Title.Questioning is a natural, instinctive, second step that most learners follow. In the scanning process, certain questions naturally arise. These should be noted in a short list of questions to be answered through reading. The questioning procedure helps the reader stay focused.
Reading occurs very rapidly if a systematic plan is followed:
First, determine the main idea from the title, the first paragraph, and the last paragraph.
Second, determine if a large subject is divided into smaller subjects with some outlining scheme.
Next, follow the title, introduction, body, conclusion rule to find the main idea of each smaller section. Each smaller section can then be scanned for keywords. Keyword recognition signals the reader to pay closer attention for critical definitions and ideas that follow.
Finally, review as often as necessary to keep focused. Outlining and note taking often help.
Reviewing new material on a strict schedule is necessary to solidify new material in the memory, and to transfer it from short term memory to long term memory.
Forgetfulness is a matter of periodic review. Memorization through repetition and forgetfulness follow a similar pattern. Each is gained or lost by halves for the same time period. The following graph illustrates the phenomenon.
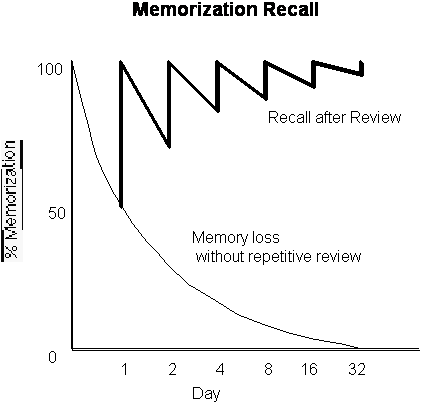
The memory loss/recall increase with review phenomenon has been verified many times. [3]
Generally memory is lost by one-half for each doubled time increment. One day after first learning one-half is lost. By day two, one-half of that remaining memory is lost, and by day four, one-half again is lost. By day four, only one-sixteenth of the original memory is intact.
At a similar rate, with review after one day only one-half of the material that was reviewed will be lost. If reviewed again on day two, the amount lost is again divided by two. If reviewed six times in a thirty-two day period, the about retained will be more than ninety-eight percent and the amount lost will only be about two per-cent in the next thirty-two days versus fifty per-cent in one day.
* * * * *
MEMORIZATION
Three common ways of remembering are: repetition, association, and exaggeration. [4] An similar skill is outlining, and samples of various outlining styles can be found in Appendix 1.
Repetition is the key to long term memory. Physiologically, when brain cells are activated by the memory process, the nerve cell coating, known as the glial sheath, increases in thickness and becomes thicker and thicker with each repetition, strengthening the electrical pathway in brain that constitutes memory. In addition, when associations between parts of a thing remembered are formed, the nerve cell body sends out axon runners to other associated memory cells. These axon runners from one cell connect through synapses to dendrite runners on other cells. As the axon-dendrite pathway is used repetitiously, the surrounding glial cells become larger and more tightly wrapped around the electrically conductive axon-dendrite pathways, thereby transforming the memory from a short-term memory to a long-term memory. [5]
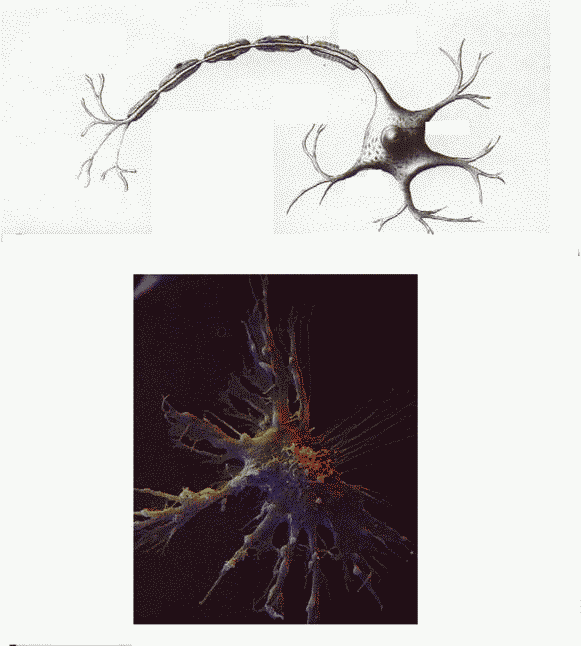
Memories of similar objects reside in nearby regions of the brain, while memories of exotic or exaggerated objects are farther away. By forming memories with creative and unusual associations, many more pathways are established, much like a spider weaving a bigger and bigger web, in which each part leads to the center by many interconnected pathways.
Memory links are also established when a variety of sensations and muscular activity are engaged. Indeed, some people seem to be more proficient at learning by either seeing, hearing or writing, but no one method can provide the more numerous pathways provided by all three in combination.
Memory is enhanced not only by repetition, but also by association and exaggeration of certain features of the object. Many memories are recalled as series of objects. For instance, a memory device to remember four common logical fallacies is a picture of the Earth, with the green continents and blue oceans, viewed from outer space with a flight of white geese circling around it. This image is used to recall the statement "geese circle every continent." The first letters of that statement (gcec) stand for the logic fallacies of generalization, circularities, either/or, and cause and effect. (These fallacies are discussed in detail in a later chapter.)
Size, also, seems to play a role in memorization. During the Middle Ages, memory contests were held annually. In one, the winner remembered one hundred thousand sequential items. [6] A time-proven memory method from the Middle Ages is association of abstract ideas to large objects. The objects used for trigger recall seem to need to be about the size of a human, so that, if we were blind, we could identify the object by touch. Large objects in the memory seem to engage muscular memory areas as well as sight memory areas in the brain and expand the memory web. For instance, remembering the points of a speech about a military battle might involving walking from one room to another in a familiar house. In the first room a ship's anchor is propped up in a corner, in the next room is a cannon, in the third room is a large telescope, and the in the fourth room is a horse. This sequence of anchor, cannon, telescope, horse might remind the speaker that the speech is about a ship being bombarded from the shore by a cannon; and that the cannon was captured when a scouting party saw the cannon through a telescope and sent for the cavalry.
Imagining numbers as objects in three-dimensional space is a very powerful way of remembering a series of numbers. This also seems to engage muscular memory. For instance, we might imagine block numbers for Pi, 3.1416. These numbered blocks should be about four inches high and one inch thick and should be imagined rotating in space about two feet to the front and about six inches above eye level. We can imagine them rotating slowly in a circle through an entire revolution. As they turn, we can mentally reach out and feel them with our fingers on every side. Such exercises, involving three-dimensional objects in space and muscles, allow the associated memory cells to form many, many more links than just a single glance at written numbers will form. Additional associations not only form more axon-dendrite connections, but also cause an increase in the surrounding glial sheath of the brain cell.
* * * * *1. Mindil, Phyllis. Power Reading. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1993.
(return)
2. Robinson, Francis P. . Effective Studying. 4th ed. New York: Harper and Row, 1970.
(return)
3. Spitzer, Herbert F. "Studies in Retention". Journal of Educational Psychology. Vol. XXX (Dec. 1930) No. 9.
(return)
4. Minninger, Joan. Total Recall—How to Boost Your Memory Power. Emmaus, Pa: Rodale Press, 1984.
(return)
5. Neural mechanisms of learning and memory. Mark R. Rosenzweig and Edward L. Bennett, eds. Cambridge, Mass. MIT Press, c1976.
(return)
================================6. Spense, Jonathan D. The Memory Palace of Matteo Ricci. New York: Penquin Books, 1984.
(return)
PRACTICAL PROBLEM SOLVING
Sequential Problem Solving is a labor of love for all students who seek success and for the parents and teachers who guide them. Sequential Problem Solving also provides the lifelong-learner with the satisfaction of being able to measure his performance.
The goal of Sequential Problem Solving is to provide learners with a road map for successfully making decisions. Students can began their adult lives with a framework that will help them pick noble goals, know themselves, and be prepared for dealing with life's villains. They can thus achieve peace and joy, and can be prepared for making life's hard decisions as well.
Young people often dream of a loving spouse and joyful children. Older people dream of success in business. Still others dream of securing a suitable retirement. Whatever the age or the dream, the problems, of making dreams come true, share some similarities.
People solving problems share certain common steps in resolving those problems and face certain common difficulties. How do we develop solutions? Where do we get information to work with? Who should we trust for advise? At what point should we make a decision? What are the alternatives?
Study leads to success, and organization builds bridges to the future. Organized systematic thinking requires effort, and the effort is justified by predictable success. This is contrasted to happenstance decision making based on impulsiveness and wishful thinking. Sequential Problem Solving is about organized thinking, and justifying decisions based on solid facts, rather than on impulsiveness or emotional indulgence. Growing to maturity is about planning rather than acting on impulses or instant gratification. Instant gratification often has costly consequences that forethought might have averted. Sequential Problem Solving is about making dreams come true while minimizing the hidden costs.
I remember well the magic of that first romantic glance across a crowded ballroom, the guileless smile and downcast eyes that instantaneously made my heart skip a beat. I remember the soul stirring melody of Band of Gold and the lingering smell of peaches and the gentle winds against my ears on a pleasant summer night. Sequential Problem Solving is about memories and dreams, making them come true, and keeping them alive.
Sequential Problem Solving is about becoming both a success and a lifelong-learner. Problem solving has two aspects: physical problems in a scientific environment and personal problems in a spiritual inner world. This book uses well known classical literary selections as models for personal decision making and character development. These works were chosen primarily due to their ready availability.
Part of the fun of sequential problem solving is mentally rewriting stories to have more favorable outcomes. We imagine favorable outcomes naturally, but successful people do so in a more systematic fashion, that makes logical outcomes more certain. Using realistic logic rather than wishful emotion requires that we know ourselves, know our values and where they came from, and know clearly what our basic goals are in life. Sequential Problem Solving systematically outlines those aspects of our spiritual inner selves that play a part in our decision making and, largely, determine our success.
Sequential Problem Solving explores the nature of personal internal conflict and how literary characters change in the course of stories to overcome personal weaknesses. Successful learners learn to recognize their own internal conflicts and learn that courage is a skill anyone can learn to re-direct their own destiny.
The first step in the adventure of becoming courageous is to write down a philosophy of life: what we want to achieve and how we plan to treat other people. A few words will do: I want to be happy, healthy, wealthy, have a loving companion, help others, etc.
Everyone should develop, write down, and periodically review their philosophy of life. If we are going to be successful, we need to have a systematic way of going about it. What do we know today about effective ways of becoming educated and successful?
At this point in time, my own philosophy for education has 11 parts.
First, learning has three basic components: specialized knowledge, basic thinking skills, and mature thinking skills. [1] In the study of Dickens' Great Expectations, "specialized knowledge" includes Pip's turbulent relationship to his sister and to her husband Joe. "Basic thinking skills" include the student's memorization of the various characters and the sequence of the plot in the story. "Mature thinking skills" include the student's analysis of Pip's internal conflict and how Pip overcomes his internal weaknesses. Mature skills might also include the creation of an alternative ending of how the story could have achieved an even more satisfactory ending. This story is unique in that there are two published endings: one, the author's original ending, and the second written at the insistence of the author's newspaper editor. These alternative endings illustrate how we can create an alternative environment and make our dreams come true. Sequential Problem Solving is about finding alternative solutions to problems and executing well researched plans.
Second, students learn to trust their own ability through success, and the teacher can help to insure that success. Success can be assured by tailoring the curriculum to the student. The student with severe prior knowledge deficits can usually be rapidly remediated by learning basic thinking skills first: for instance, the basic memorization techniques, note taking, outlining, and free association recall techniques. (These are discussed in detail elsewhere.)
Students should be aware of what they learn and feel pride of accomplishment. They should recognize for themselves when they achieve success in learning. They should learn to constantly monitor their own performance and the success of their strategies.
Learning occurs in well ordered ways:[2] first, the student gains understanding of what is read or the teacher explains, then memorizes the facts of the subject in order to analysis the information later through comparing and contrasting. Next the student may use the information to create something new, and finally he should use the memorized information to evaluate his own performance. This sequence is known to teachers as Bloom's taxonomy. [3]
Students need guidelines for making decisions. Those decisions may involve physical, scientific problems, or they may involve interpersonal problems, social values and moral decisions. Students should learn a systematic workable framework for making decisions. All students should develop the ability to evaluate their thought processes as a learned skill. The mature learner should be able to recall the steps of scientific problem solving, recognize specific personal values and character traits, and remember the tests for sequential steps in moral decision making. Students should then be able to use apply those mature thinking skills to first literary scenarios and then to real life problems. Studies of literature enable the student to extend the analysis to television drama and ultimately to real life and to subsequently imagine a variety of suitable alternative outcomes.
Students should learn to recognize and control certain biological feelings. A student should know how the human brain is organized and recognize those times when animal-like impulses jeopardize more mature, rational thought. A student should also be able to recall and use basic information about basic nutrition, rest, and exercise, in order to minimize the danger of thoughtless impulsiveness.
Students should develop a sense of belonging to a caring, helpful humanity, and develop their own short and long term goals in achieving peace and joy through helping others in a responsible manner.
Students should learn the dynamics of basic childcare and the importance of continuous parental attachment in the first two years of a baby's life. Students should be aware of how "unattached" children are set up for failure and antisocial behavior disorders, by poor bonding with the parent in the first few months and years of life.
Students should be prepared to deal with manipulative people. Students should learn how to recognize people without a conscience. Students should have strategies for managing interpersonal relationships, both good and bad.
Students should have a knowledge of the religions of the world and develop a toleration for other people.
Finally, students should become citizens of the world, dedicated to helping others while making their own dreams come true.
Developing and maintaining a systematic philosophy of life entails becoming a lifelong learner.
* * * * *Learning has three basic components: specialized knowledge, basic thinking skills, and mature thinking skills.
Specialized knowledge is that part of a study that must be memorized. This "disciplinary based knowledge" contains unique terms and definitions. Language studies have their unique terms: nominative, comma, plot; mathematics has its: tangent, sum, parabola, etc. These are terms that must be memorized in order to understand and use the subject matter.
Basic thinking skills include memorization techniques, the stream of consciousness technique, outlining, note taking, rapid reading, scanning for main ideas and keywords, questioning, and reorganizing.
Mature thinking skills include procedures that require specialized knowledge and basic thinking skills, like applying the sequential steps of problem solving and following the sequential tests for moral decision making.
* * * * *Both creative writers, artists and scientific problem solvers use the stream of consciousness or free-association skill. This skill is also known as gestation, mulling things over, and getting a handle on things. The process begins by letting our thoughts flow freely and then sorting out the ones useful to our problem from the many that came to mind. Often many of the random thoughts that come to mind have no apparent connection to the problem; they are merely connected like circular links in a spider's web to threads that interconnect with others and run toward the center of the problem. The free association technique begins by trying to think about nothing in a relaxed, tension-free environment. Try as we might, something always intrudes on our consciousness. It may a line running toward the center of the web or it may be a seemingly meaningless, circular line. Every thought should be written down as it comes to mind, and the task of thinking about nothing begun anew. After ten or fifteen minutes, the train of intrusive thoughts usually begins to slow down, and we can then take the list of seemingly unrelated thoughts and sort out the ones that relate to the problem. The next step of brainstorming is to take the free association / stream of consciousness list and circle the words that pertain to the problem, and connect them with "web" lines into "clusters." These crude webs and clusters can then be reconstructed into a more legible outline. (Several styles of outlining are illustrated in the Appendix 2.) This outline can then be used in the subsequent steps of problem solving. The subsequent steps of the problem solving procedure involve hypothetico-deductive reasoning and is a part of the scientific method.[4]
* * * * *A. Research—library, Internet.
B. Ask someone knowledgeable.
C. Brainstorm: free association / stream of consciousness, web and cluster, outline.
3. Develop several alternative solutions.Problem Identification is the first step of problem solving. In life, personal problems are often complicated by outside challenges. In literature, these forces are called external conflicts. The external conflict may be man challenged by nature, man embattled by society, or one man opposed by another man. In science, problems are often exclusively matters of a physical nature and the external conflict is man being challenged by nature.
Internal conflicts have a personal nature. By comparing personal internal conflicts to Aristotle's structure for dramas, these conflicts can often be recognized. Aristotle's drama structure divided the play into five acts with a hero, a villain, an external conflict and climax, and an emotional cleansing involving an internal conflict. Real life internal conflicts often involve character traits and values that are easily identified by this method.[5] (Character traits and values are discussed in the section on interpersonal relationships.)
* * * * *The preferred order for gather facts is based on the order of reliability: library research, asking someone knowledgeable, and brainstorming.
Facts should be tested for logic, emotional fallacies, and the credibility of "expert" witnesses. Facts gained from research in a library are easiest to verify, and other methods of gathering facts must often be re-verified through library research. Logical and emotional weaknesses of arguments can often be recognized by the use of certain fallacy recognition checklists.[6] The most widely used of the fallacies is the over or under generalization: everyone (all, without exception, none, never, no one) rode a bicycle when only two years old. [7]
* * * * *A. SINGLE CAUSE fallacy—The streets are wet, therefore it has been snowing.(This discounts other causes like rain.)
B. GUILT BY ASSOCIATION—He has a friend that is a Japanese, therefore he must be Japanese in his soul.
* * * * *i. SARCASM.
ii. CYNICISM.
* * * * *Credibility fallacies are those in which uncertified people present themselves as experts: the famous actor dressed as a doctor recommending a certain medicine. The actor is not a trained professional and has no professional credibility.
FACT AND OPINION.Certain keywords can be often be used to differentiate facts from opinions.
1. Generalizations. All inclusive or all exclusive terms that usually have exceptions: everyone, everything, no one, never, always:It always rains in the summertime. (This does not take into account long droughts or geographic locations where rain rarely falls.)
Everyone drives a Ford.
2. Statements about the future:We will never go there.
3. Statements of opinion:It seems to me.
In my opinion.
4. Statements using the emphatic "to be" words. Is, are, was, were, etc. are often facts that can be proven either true or false, but are not necessarily as true as the "is" implies.He is a genius.
For the purpose of gathering information in problem solving, facts are statements that can be readily verified as true or false; opinions cannot be quickly verified. In problem solving, the practical ability to prove something true without a great deal of effort is the key to practical truth. A statement that might merely hold the possibility of being proven true is, for all practical purposes, an opinion until it is proven true.
* * * * *Deductive reasoning [9] is stating a series of valid relationships with a conclusion about them:
When it rains the streets get wet. It is raining. Therefore the streets are wet.
Several types of reasoning fallacies exist: (1) formal deductive fallacies, which occur because of an error in the form of the argument, and (2) informal fallacies that contain false content.
The INFORMAL FALSE CONTENT FALLACIES are listed in Appendix 4 and include:
LOGIC ERRORS.The emotional tactics often include cynicism or sarcasm and are sometimes used to belittle another person. The effect is to make them feel worthless and unloved. This is an emotional fallacy that attacks a person's need for love and belonging. [10] This is discussed in greater detail in the section on Internal conflicts.
Sometimes debaters attempt to evade answering an argument using the "red herring" diversion. This tactic was named for game poachers that used a strong smelling fish to mask their scent from dogs used by game wardens trying to apprehend them. This tactic introduces another issue that diverts the discussion. It is often logically unrelated to the issue, and is often an emotional attack directed at the other person.
* * * * *1. Beyer, Barry K. "Developing a Scope and Sequence for Thinking Skills Instruction". Educational Leadership 45(April 1988): 26-30.
(return)
2. A Committee of College and University Examiners. "Educational Objectives and Curriculum Development". Taxonomy of Educational Objectives—Handbook 1: The Cognitive Domain. Benjamin S. Bloom, ed. New York: David McKay Company, Inc., 1956.
(return)
3. A Committee of College and University Examiners. "Educational Objectives and Curriculum Development". Taxonomy of Educational Objectives—Handbook 2: The Affective Domain. Benjamin S. Bloom, ed. New York: David McKay Company, Inc., 1956.
(return)
4. "The Galileo Affair", Owen Gingerick, American Scientific, August, 1982, #247, p.132-138.
(return)
5. Aristotle. Rhetoric and the Poetics. F. Solmsen, ed. New York: The Modern Library, 1954.
(return)
6. Critical Thinking and Reasoning: a handbook for Teachers. Albany: SUNY, 1976.
(return)
7. "Classifying Fallacies Logically", Ludwig F. Schlecht, Teaching Philosophy, March, 1991, 14:1, p.53-656.
(return)
8. Maslow, A. H. Motivation and Personality. New York: Harper and Row, 1954.
(return)
9. Critical Thinking and Reasoning: A Handbook for Teachers. Albany: The University of the State of New York, 1976.
(return)
=============================10. Maslow, A. H. Motivation and Personality. New York: Harper and Row, 1954.
(return)
Developing solutions should take into account time, material and manpower. How much time is available to solve a problem? Are the materials available? Is the manpower available?
TIME.How much time is available? Often problems are best solved by using "Kentucky windage." Artillery gunners use the expression, "One over, one under, one dead center." This refers to making gross adjustments rather than walking a solution toward a problem one small step at a time. This technique has also been called "Eliminating the extremes": walking toward the center from either end, half way at a time. This technique reduces the time required to solve a problem in a binary fashion by halves, rather than in arithmetic progression one small step at a time.
Often the first solutions tried don't work. We may learn more facts about problems as we try to solve them. Many times a problem requires re-defining and the entire nature of the solution changes from one trial to the next. In science, every experiment is valuable because what is disproven is as valuable as the final solution. A disproven solution reduces the possibilities by providing answers about what is not possible.
We need to take into account problems that will arise. It is useful to double or triple the initial time estimate when beginning new projects. It is prudent to plan on finishing the job in one-third to one-half of the time we would like to finish the job. This is particularly true with artistic projects; artists often want to add one final touch, and one more touch ad infinitum (the "Michelangelo" dilemma).
Timing for the various elements in a job can often be charted beginning with the first thing needed to be done and ending with a review of the project and future planning. Such charts are easily constructed on spreadsheets with calendar dates in vertical columns and tasks in horizontal rows. This form of time chart is a marching calendar. Initially, the chart can also be used to back schedule material purchase for future delivery. As sequential tasks are completed, the consecutive days are highlighted. This provides a rapid visualization to the project planners of the status of the project.
Project Calendar.
Task.
Initial planning.
Gather information.
Pick team.
Make drawings.
Assemble materials.
Make prototype.
Review prototype.
Manufacture actual product.
Evaluate project.
Plan follow up.
* * * * *
MATERIAL.
Are the materials available? Can we afford the cost of the materials? Sometimes it is possible to make an "first piece" or "practice piece" out of inexpensive materials. Practice pieces are helpful to learn practical manufacturing methods. Producing detailed drawings and listing manufacturing steps often save time and material in the long run. Practice pieces made of soft and easy to work material, like balsam wood, also serve the purpose of providing an actual mock up that can be quickly modified by cut and paste methods. The practice piece usually does not have to be pretty, only functional. It provides an idea of what changes need to be made before expensive or hard to procure materials are used.
* * * * *Is sufficient manpower available to execute the plan? Are the talents of the available manpower matched to the task? [1] Are the available people qualified to perform the tasks? Are the men being lead by the best method? Several alternative methods exist for leading or managing workers on a project. These will be discussed in the section on leadership.
* * * * *1. Gardner, Howard. Frames of Mind: The Theory of Multiple Intelligences. New York: Basic Books, 1983.
(return)
Often complex or new tasks become learning projects, in themselves, to try to more accurately identify the problem, and to gather sufficient facts through failure in experimentation to make progress. Projects should include ongoing evaluation and re-planning. Old World craftsmen, the master craftsmen of yesteryear, had a guiding principle that continues to have merit: "Any job worth doing is worth doing well." Doing a job well often means making a final copy after revising the rough draft.
* * * * *Leaders should remember that several approaches to leadership are available. No one style is satisfactory for all situations.
* * * * *Three basic leadership styles exist. They are the authoritarian model, the teacher model, and the team work model. [1]
The authoritarian model is useful for situations requiring immediate compliance by a subordinate. Soldiers occasionally use the authoritarian style to demand instant obedience. It is most useful in dangerous situations where hesitation in complying might be disastrous; for instance, when a child is daydreaming and in danger of walking off of a sidewalk curb into automobile traffic. In business situations, this style is not often used because the authoritarian leader is often destined to fail: "micro-management" often has a belittling effect on subordinates, who subsequently rebel, and failure follows for three reasons: the authoritarian leader often doesn't have the expertise, time, or enough energy to do all of the jobs himself job without other's help. The authoritarian leadership style is seldom useful except in emergency situations.[2] (It has been said that a raised voice with someone older than five is usually inappropriate.)
The teaching leadership model is more useful because the people doing the job are contributors. The teacher offers advice and monitors progress.[3]
The team work leadership model is sometimes the most useful. This model works when the students become as knowledgeable as the teacher and each can and will do the other's job. This model is often seen when someone realizes a job needs doing, and does it without being told to do it. These people are conscientious "self-starters."
* * * * *1. Tannenbaum, Robert and Warren H. Schmidt. "How to Choose a Leadership Pattern." Harvard Business Review 36(March-April 1958): 95-101.
(return)
2. Fiedler, Fred E. "The Trouble With Leadership Training Is That it Doesn't Train Leaders." Psychology Today 6(February 1973): 23-30.
(return)
=================================3. Goodall, H. Lloyd, Jr. Small Group Communications in Organizations. 2nd ed. Dubuque, IA: Wm. C. Brown, 1990.
(return)
Western World values and ideas of dealing with interpersonal conflict originate in the Code of Hammarabi and the Mosaic Code.
King Solomon in the Bible, following the Ten Commandments of Moses, offers some practical suggestions for dealing with interpersonal conflict.
In Solomon's Book of Proverbs, one of Solomon's main themes is drawing a consistent distinction between the wise man and the foolish man. He characterizes a foolish man as someone who neither asks for advise nor accepts it. He further characterizes the foolish man as someone who is scornful, divisive, quarrelsome, and mocking of other's efforts with cynicism and sarcasm.
Solomon's advise for dealing with scornful people has three steps. The first step is to try counseling with them in private, one on one. Failing that, the second step is to counsel with them again, but with two people, together, advising the third. The final step is to cease relations.
Solomon's three steps are seen today in practical statesmanship. We should remember that today's enemy is tomorrow's friend. Member nations of the United Nations generally apply this same three-step plan that ends in economic sanctions being applied by the United Nations as a whole. Sometimes even ceasing relations with another is not enough and force of arms must be taken to protect weaker neighbors from aggression.
Whether with neighbors or nations, armed conflict is ultimately sorrowful. It is an admission that patient diplomacy and logic have not been successful. It is premeditated violence to protect the weak. Many people, still developing in religious maturity and understanding, feel torment when violence is necessary, because their religious understanding does not extend beyond helping "all" others. It is a question of who is helped and why. Some people too choose to pass from this life as martyrs. Others feel compelled to stay until the end and protect the weak like a shepherd keeping predatory dogs away from the helpless lambs. There may be a time for each course of action.
The confusion between religion and forcing our will on others is caused by our understanding of what helping others means. If we help others to hurt someone, we become harmful ourselves. We become "Enablers" [1] to those hurting others. Without our consent, the aggressor could not have taken advantage of his weaker neighbor.
The Eastern religions, particularly Zen Buddhism, which is intimately associated with the Samurai warrior of Japan, take great care to teach tranquility and self-control in the use of force. Anger is not a part of thoughtful action.
Aikido, The Way of Harmony, teaches tranquility in the use of force, and compares it to the calm in the eye of a hurricane.[2]
The great Christian pastor, Dietrich Bonhoffer, pointed out that "just causes" for anger did not exist in the earliest accounts of Christ's Sermon on the Mount.[3]
* * * * *1. Miller, Angelyn. The Enabler.—When Helping Harms the Ones You Love. New York Ballentine Books, 1988.
(return)
2. Stevens, John. Abundant Peace—the Biography of Morehei Ueshiba, the founder of Aikido. Boston: Shambhala, 1987.
(return)
* * * * *3. Bonhoeffer, Dietrich. The Cost of Discipleship. New York: Macmillan, 1963.
(return)
Drama and literary analysis as a tool in personal problem solving.
The structure of Aristotle's Pentad [1] for five act plays is useful as a framework for solving personal problems.
1. Who is the hero? What are his weaknesses? How is he likely to fall?This five part framework is useful in separating the external foes we face from the internal conflicts that are our weaknesses.
EXTERNAL CONFLICTS.External conflicts are usually found to involve either another man, nature or society. In the man versus man conflict, another person is the adversary. In the man versus nature conflict, the adversary might be a hurricane, or the rigors involved in climbing a mountain. In the man versus society conflict, the opponent might be industrial organizations or lobby groups advocating nuclear waste disposal in the ocean.
The man versus self conflict, such as a man facing a crisis of courage, is an internal conflict.
INTERNAL CONFLICTS.Internal conflicts are man versus himself and man versus God conflicts.
The man versus God occurs when a person violates his conscience and does something that he knows to be wrong. Many religions advocate resolving the man versus God conflict by admission of wrongdoing and restitution to those harmed. There may be some people that have no conscience, and the internal conflicts they face are not, as yet, well understood. [2] Those people without a conscience are a continuing source of grief for humanity and that problem is discussed in the section on dealing with "unattached people."
The second type of internal conflict, the man versus self conflict exhibit certain human character weaknesses that can be identified with the acronym FALL: fear, arrogance, laziness, and loneliness.
Loneliness is often caused by a combination of several of the other three common human weaknesses, for instance, fear and laziness: fear of rejection while trying to find new friends and laziness in making the attempt.
Fear is a very common weakness and is related to our needs. Abraham Maslow[3] classified these needs as follows:
1. Physical safety.People must meet their immediate, basic needs for physical safety before they can meet their wishful needs for love or fulfilling a career. While we strive to behave as thinking people, with well thought out plans, sometimes we act purely as animals by instinct alone. If we are suddenly frightened by a snarling dog, we react by running or fighting, instinctively, without conscious thought. Paul MacLean describes what happens in our brains as a stepping down the evolutionary ladder and using those parts of our "Triune" brain that operates on instinct rather than thought. [4]
MacLean divides the Triune brain [5] into three parts that developed over the evolutionary eons. The oldest, which he calls the reptilian brain, controls aggression and passionate impulsiveness. The middle region, the limbic system, controls docile, loving emotions. The outer region, the neo-cortex controls thoughtful planning with an awareness of consequences and cause-effect relationships. This phenomenon is important because fear alone can inhibit successful higher level thinking by keeping the brain at the lowest (reptilian) level preparing to meet the threat. The educator Lev Vygotsky stressed the importance of creating and maintaining a risk-free environment that encourages higher level (neo-cortex) thought. [6] The growing recognition of the Triune Brain might very well have influenced world politics in the replacement of the policy of "mutually assured destruction" with a "kinder and gentler" statesmanship.
Maslow's need and MacLean's brain are both related to animal-like behavioral weaknesses when we react impulsively rather than with thought and planning, and we are more likely to act impulsively when our physical safety or food and shelter needs are threatened.
When we do act like animals, we often are ashamed because we momentarily set aside our conscience. Fear overpowers our desire to be loving because it engages lower brain centers that are not controlled by abstract thought centers in the higher levels of our brain.
How then can we act like we are created in the image of God instead of selfish, impulsive animals? We can begin by analyzing what characters in literature and drama do. We can recognize when fear, arrogance, laziness, or loneliness drives the hero's actions, and imagine how the hero might overcome his weaknesses. We can project a responsible resolution to the hero's internal conflicts. This exercise of recognizing the source of another's actions is merely an intermediate step in the learning process, however. [7] The final step is when we face our own trails, and face the need to analyze our own reactions to stress, as we have looked at those in dramas. Finally, we can plan our own future and make it happen, just as we did with alternative endings to conflicts in dramas.
Occasionally, people face moral choices that seem to confusing to be solved, and the thinking brain tries to step down a notch. It either takes a passive emotional position with MacLean's limbic system, or an impulsive aggressive position with the reptilian system. At these times, a checklist for moral decision making can provide a framework for keeping our actions in the realm of planned activity rather than impulse.
THE STEPS OF MORAL DECISION MAKING.Moral decision making involves several growth steps in reaching maturity.
Stanley Kohlberg [8] provided us with a framework for making moral decisions:
Age Test Question.Religious people often experience great internal conflict when faced Many religions advocate gentleness and helping others, as well as protecting the weak from harm: a seeming contradiction. Does one have priority over the other? Part of the answer may involve the Triune brain and the absence of thought involved in impulsive aggression. Sometimes helping others may involve protecting violent people from themselves and that may require the use of force. Often gentle, kind people find the use of force quite foreign, and are especially vulnerable to harm from people that are termed "unattached." [9]
DEALING WITH THE "UNATTACHED" PERSON."Unattached" people refers to people that have a defective conscience. [10] Their actions are motivated by a lifelong distrust of others and a supreme belief in their own ability. They have no need for other people. Their brains seem to function at a very low evolutionary level, but at times they are superficially charming and persuasive. These people are manipulative and often become sociopaths, and their behavior is thought to have been molded before they were six months of age by insufficiently attentive caretakers.
"Unattached" people, people who bonded inadequately with their parents, are frequently very hard to convince with logical arguments due to their deep distrust of other people and the pattern of control battles continue throughout their lifetime. [11] This sad picture is drawn from the experiences of those professionals who deal with them on a regular basis. The sociopath's irreversible behavior patterns seems to be founded, physiologically, in well established repetitive memory pathways. Perhaps modern science will find ways to help such unfortunate people, possibly through more effective chemical intervention that makes a person feel less threatened, so that they can learn more productive way of treating other people.
Mercifully, some spiritually enlightened people are able to reach older "Unattached" people and to help them to learn to trust others and achieve that measure of "peace that surpasses all understanding" spoken of by the Apostle Paul in his Letter to the Phillipians in chapter 4, verse 7: "And the peace of God, which passeth all understanding, shall keep your hearts and minds through Christ Jesus."
We are all saddened when others fail to respond to logic and kindness and the use of force is necessary, but the periodic necessity of using force to protect others is often unavoidable. Our own internal conflicts of loneliness brought on by dealing with sociopaths is perhaps brought on by our own fear of not being loved by others. The realization of that phenomenon might help us to resolve our own internal conflict in dealing with the manipulative sociopath.
One of the problems with dealing with unattached people or sociopaths is the difficulty of recognition. At one time, they seem friendly, intelligent, well adjusted, and exhibit apparent sincerity in wanting to be a friend to others. At other times, their behavior seems to snap over, instantaneously, to that of a selfish ten year old. In Kohlberg's view of moral decision making, the age of ten is when a person begins to use the Everyone Rule (what would the world be like if everyone did the action in question). Sociopaths often do not consider others, rather seek instantaneous gratification of their own impulsive needs, much like a ten year old.
Sociopaths are often superficially charming, yet frequently exhibit certain adverse character traits. They are:
untrustworthy vs trustworthyOther peculiar traits include speech pathologies, and primary process (crazy) lying. Speech pathologies include "baby" talk by an older person. Crazy lying includes the child caught with a stolen candy bar in his hand who replies, "What candy."
While often charming, unattached people are basically self-centered and lack values that guide their conduct with other people.
INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS—VALUES.Sequential problem solving and dealing with interpersonal relations involves weighing various values and determining what is appropriate or inappropriate behavior. It is, therefore, desirable to have a firm grasp of our own values. What does society expect of us? What do we expect of others? What do we expect of ourselves?
The values of the English speaking countries came largely from Great Britain. The English Common Law system and the Judeo-Christian values expressed in it originated, in part, with King Arthur and the Knights of the Roundtable.
King Arthur and his knights left us with some simple guidelines: THE KNIGHT'S MOTTO—BE ALWAYS READY.
THE KNIGHT'S CODE:
On my honor I will do my best—
To do my duty to God and my King;
To obey the Knight's Laws;
To help other people at all times;
To keep myself physically strong, mentally alert, and morally straight.
THE KNIGHT'S LAWS. The Knight is to be:
Trustworthy—I will not lie, cheat, or steal.
Loyal—I will not tolerate those who lie, cheat, or steal.
Helpful—I will help other people at all times.
Friendly
Courteous
Kind
Obedient
Thrifty
Cheerful
Brave
Clean
Reverent
The underlying values of Knighthood and the Bible were eventually passed on to the Scouting movement for boys and girls by General Sir Baden-Powell about 1908. [12] The priority expressed in the Knight's Code is God, country, others, self—the same sequence as in THE TEN COMMANDMENTS OF MOSES:
1. Thou shalt have no other gods before me.The Ten Commandments and the underlying message of the Bible, of helping one another, provide us with the framework for appropriate interpersonal relationships. When the human factor in problem solving is kept in mind through a list of values and a code of conduct, personal problem solving becomes a matter of analyzing internal conflict (fear, arrogance, laziness, or loneliness). When a problem presents itself and action seems slow, it is helpful to recognize the ways people evade problems.
PROBLEM SOLVING EVASIONS.1. SUBLIMATION—sublimation is a compromise involving the gestation phase of problem solving. This often includes hobbies or other relaxation things that tend to disengage the left brain and allow the right brain greater autonomy. These relaxation devices allow the right brain to both synthesize new solutions and recall long unremembered solutions, as well as create new things for the fun of it. This activity occurs naturally. Sometimes sublimation activities are a compulsion driven by feelings of abandonment, as are other compulsions like substance abuse, gambling, and compulsive spending.
2. ANGER—anger is often an immature reaction to frustration or stress, and is not considered a part of higher neo-cortex thinking; it is rather a reptilian reaction in MacLean's Triune Brain scheme.
Anger is also a step in the Grief Process described by Elisabeth Kubler-Ross that progresses through denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and finally acceptance.
3. REGRESSION—a return to the "Good Ole" Days. This problem evasion mechanism is farther from the problem solving pathway than anger. It involves the return to behavior of an earlier age.
4. DISTORTION—these problem evasion mechanisms pass even farther from problem solving toward problem evasion.
i. PROJECTION—attributing unacceptable thoughts and feelings to someone else: "They don't like me."
ii. REACTION FORMATION—forming good feelings for a tyrant to minimize bullying: the terrorized victim reaction.
iii. INTELLECTUALIZATION—continuing research to find fool-proof solutions, rather than taking a chance at failure.
iv. DISPLACEMENT—prejudice, racism. Sarcasm and cynicism are frequently used in expressions of superiority over others.
5. REPRESSION—This is the final evasion of problem solving and the most severe. It is a denial mechanism that involves blocking from consciousness that the problem ever existed.
Problem Solving Evasions.* * * * *
1. Aristotle. Rhetoric and the Poetics. F. Solmsen, ed. New York: The Modern Library, 1954.
(return)
2. Magid, Ken and Carole A. McKelvey. High Risk: Children without a Conscience. New York: Bantam Books, 1987.
(return)
3. Maslow, A. H. Motivation and Personality. New York: Harper and Row, 1954.
(return)
4. MacLean, Paul. Triune Concept of the Brain and Behavior. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1973.
(return)
5. Sagen, Carl. The Dragons of Eden., New York: Ballantine Books, 1977.
(return)
6. Vygotsky, Lev. Thought and Language. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1962.
(return)
7. A Committee of College and University Examiners. "Educational Objectives and Curriculum Development." Taxonomy of Educational Objectives—Handbook 1: The Cognitive Domain. Benjamin S. Bloom, ed. New York: David McKay Company, Inc., 1956.
(return)
8. Kohlberg, Lawrence. "Moral Education for a Moral Transition." Educational Leadership 32 (October 1975): 46-54.
(return)
9. Magid, Ken and Carole A. McKelvey. High Risk: Children without a Conscience. New York: Bantam Books, 1987.
(return)
10. Unmasking the Psychopath—Antisocial Personality and Related Syndromes. William H Reid, Darwin Dorr, John I. Walker, Jack W. Bonner, eds. New York: W.W. Norton, 1986.
(return)
11. Cline, Foster. Understanding and Treating the Severely Disturbed Child. Evergreen, CO: Evergreen Consultants in Human Behavior, 1979.
(return)
* * * * *12. Handbook for Boys. New York: Doubleday-Page and Co., 1911.
(return)
APPENDIX 1
Outline Styles
1.I.
i.
ii.
iii.
II.
III.
IV.
APPENDIX 2.
PERSUASIVE ARGUMENT FORM.
First establish topic, audience, and personal position. Then gather information and organize the argument.
1. Introduction.Arrange these points (A) second best point, (B) weakest point, (C) strongest point. This is known in the study of rhetoric as the Nestorian Order. It achieves interest at the beginning and finishes strong.
2. The Body.Deductive reasoning is stating a series of valid relationships with a
reasonable conclusion.
When it rains the streets get wet.
It is raining.
Therefore the streets are wet.
[1]
Several reasoning fallacies exist: (1)formal deductive fallacies, which occur because of an error in the form of the argument, and (2) informal false content fallacies.
(1) A formal deductive fallacy might switch a premise with the conclusion:
The streets are wet.This conclusion is fallacious because there are other reasons that could have caused the street to be wet: snow melt, a street sweeper, etc.
(2) Several informal false content fallacies are: LOGIC ERRORS:
* The "STRAW MAN" deception.This is deceptive attack on an opponents position using a similar but different position.
"The President states that he is a 'Peace' president, but will help those in need. No doubt he will withdraw the NATO peace keeping force from Bosnia and send them to Somalia to assist with the famine relief."
What the president meant to say was that he will seek all reasonable diplomatic solutions to international aggression but will not abandon international treaties and will assist other nations with military forces.
* The "FALSE DILEMMA" deception.This deception often presents an argument so horrible that it is an unacceptable alternative, and the speaker's argument is presented as the only alternative.
"Ebola virus has been accidentally released in Merryman Corporation research facility in Maryland. One way to destroy it is to drop a nuclear bomb on the facility. Another alternative is to accept the proposal of the Paladin Corporation to take over supervision of the contract granted to the Merryman Corporation. Paladin estimates that they can decontaminate it with lethal gas for a mere ten million dollars."
* The "DOMINO THEORY" deception.The domino theory deception makes the claim that if one thing happens another will invariably follow.
"If South Vietnam falls to the Communists, every other nation in Southeast Asia will follow, including Australia."
* The "TWO WRONGS MAKE A RIGHT" deception."It is all right to execute prisoners because South Africa does it too."
EMOTIONAL TACTICS.This fallacy is known as the AD HOMINEM fallacy.
"The mayor proposes opening a day care center for city hall employees. The mayor was once divorced. The mayor is not competent to make family decisions."
The mayor's willingness to please his employees and his administrative competence are diverted with a personal attack.
* The "COMMONLY ACCEPTED PRACTICE" deception.This deception often is designed to make an action seem biased or prejudicial.
"It is common practice to replace computers in business every five years. The military even has a policy to that effect ."
* The "APPEAL TO PITY" tactic."If welfare recipients are required to work, many recipients will not be able to watch television as much."
* The "INFALLIBLE TRUTH or CLICHE" deception. "This meal is not well seasoned. Too many cooks spoil the soup."The emotional tactics often include cynicism or sarcasm and are used to belittle the other person. The emotional tactics are often used to make another person feel worthless and unloved.
* * * * ** * * * *1. Critical Thinking and Reasoning: A Handbook for Teachers. Albany: The University of the State of New York, 1976.
(return)
Research Skills.
Edwards, Betty. Drawing on The Right Side of The Brain. Los Angeles: Tarcher, Inc., 1979.***END OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK SEQUENTIAL PROBLEM SOLVING***
******* This file should be named 16547-h.txt or 16547-h.zip *******
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/1/6/5/4/16547
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is subject to the trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.net/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
This particular work is one of the few copyrighted individual works
included with the permission of the copyright holder. Information on
the copyright owner for this particular work and the terms of use
imposed by the copyright holder on this work are set forth at the
beginning of this work.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.net),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS,' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, is critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Each eBook is in a subdirectory of the same number as the eBook's
eBook number, often in several formats including plain vanilla ASCII,
compressed (zipped), HTML and others.
Corrected EDITIONS of our eBooks replace the old file and take over
the old filename and etext number. The replaced older file is renamed.
VERSIONS based on separate sources are treated as new eBooks receiving
new filenames and etext numbers.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.net
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.
EBooks posted prior to November 2003, with eBook numbers BELOW #10000,
are filed in directories based on their release date. If you want to
download any of these eBooks directly, rather than using the regular
search system you may utilize the following addresses and just
download by the etext year.
http://www.gutenberg.org/dirs/etext06/
(Or /etext 05, 04, 03, 02, 01, 00, 99,
98, 97, 96, 95, 94, 93, 92, 92, 91 or 90)
EBooks posted since November 2003, with etext numbers OVER #10000, are
filed in a different way. The year of a release date is no longer part
of the directory path. The path is based on the etext number (which is
identical to the filename). The path to the file is made up of single
digits corresponding to all but the last digit in the filename. For
example an eBook of filename 10234 would be found at:
http://www.gutenberg.net/1/0/2/3/10234
or filename 24689 would be found at:
http://www.gutenberg.net/2/4/6/8/24689
An alternative method of locating eBooks:
http://www.gutenberg.net/GUTINDEX.ALL
*** END: FULL LICENSE ***